A Prime Sum Circle
Arrange the numbers in a circle so that the sum of any two neighboring numbers is prime. The problem is known as the “Prime Circle Problem” and is due to Antonio Filz (Problem 1046, J. Recr. Math. vol 14, p 64, 1982; vol 15, p 71, 1983). It appears in the classic book by Richard Guy, Unsolved Problems in Number Theory, 2nd edition.
Solution
The prime circle is a Hamiltonian cycle in the bipartite graph made from the edges that exist upon satisfaction of the condition (namely, the sum is prime). In simple English, what this means is that solution of the puzzle is equivalent to finding a Hamiltonian cycle (a cycle that visits each vertex exactly once) in a graph with vertices numbered and an edge between two vertices whenever the sum of the vertices is a prime. Here is my solution in Python using the networkx library.
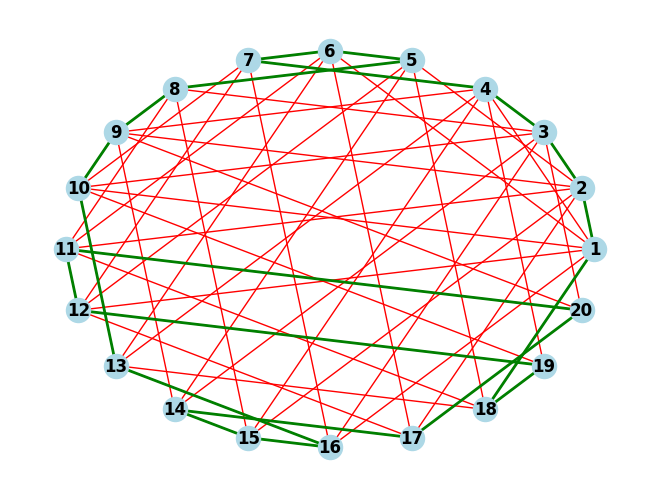
import networkx as nx
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import itertools
from networkx.algorithms.cycles import simple_cycles
from networkx import DiGraph
# Function to check if a number is prime
def is_prime(n):
if n <= 1:
return False
for i in range(2, int(n**0.5) + 1):
if n % i == 0:
return False
return True
# Create an undirected graph
G = nx.Graph()
# Add nodes
G.add_nodes_from(range(1, 21))
# Add edges between nodes if their sum is prime
for u, v in itertools.combinations(G.nodes, 2):
if is_prime(u + v):
G.add_edge(u, v)
# Initialize a variable to store a Hamiltonian cycle
hamiltonian_cycle = None
# Iteratively check each cycle
for cycle in simple_cycles(DG):
if len(cycle) == len(G.nodes):
hamiltonian_cycle = cycle
break # Exit the loop as soon as a Hamiltonian cycle is found
# Plot the graph
pos = nx.circular_layout(G) # Position nodes in a circle
nx.draw(G, pos, with_labels=True, node_color='lightblue', edge_color='red', font_weight='bold')
# Highlight the Hamiltonian cycle if found
if hamiltonian_cycle:
# Ensure the cycle is in the correct order for plotting
hamiltonian_cycle.append(hamiltonian_cycle[0]) # Make it a cycle
nx.draw_networkx_edges(G, pos, edgelist=list(zip(hamiltonian_cycle, hamiltonian_cycle[1:])), width=2, edge_color='green')
print("Hamiltonian cycle found.")
else:
print("No Hamiltonian cycle found.")
plt.show()
Two other similar problems where the hamiltonian cycle and path approach works are given below.
Neighbours form a square - 1
Write out the numbers as a sequence so that every pair of neighboring numbers sums to a perfect square. (For example, could be part of the sequence because and .)
Solution
Here is a solution using the code below: . The idea is to create a graph such that the sum of a node and any of its neighbours’ is a perfect square and check if the graph contains a Hamiltonian path.
import networkx as nx
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def is_perfect_square(n):
root = int(math.sqrt(n))
return root * root == n
def find_hamiltonian_path(graph, node, visited, path):
visited[node] = True
path.append(node)
if len(path) == len(graph.nodes()):
return True
for neighbor in graph.neighbors(node):
if not visited[neighbor]:
if find_hamiltonian_path(graph, neighbor, visited, path):
return True
path.pop()
visited[node] = False
return False
def hamiltonian_path(graph):
visited = {node: False for node in graph.nodes()}
path = []
for node in graph.nodes():
if find_hamiltonian_path(graph, node, visited, path):
return path
return None
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_nodes_from(range(1, 17))
for i in G.nodes():
for j in G.nodes():
if i < j and is_perfect_square(i + j):
G.add_edge(i, j)
path = hamiltonian_path(G)
if path:
print("Hamiltonian Path:", path)
else:
print("No Hamiltonian Path found!")
Neighbours form a square - 2
Write out the numbers as a sequence so that every pair of neighboring numbers sums to a perfect square and the first and last entries must also sum to a square.
Solution
Here is a solution . The idea is to create a graph such that the sum of a node and any of its neighbours’ is a perfect square and check if the graph contains a Hamiltonian cycle.
import networkx as nx
import math
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
def is_perfect_square(n):
root = int(math.sqrt(n))
return root * root == n
G = nx.Graph()
G.add_nodes_from(range(1, 33))
for i in G.nodes():
for j in G.nodes():
if i < j and is_perfect_square(i + j):
G.add_edge(i, j)
def hamiltonian_cycle(graph):
for cycle in nx.simple_cycles(graph):
if len(cycle) == len(graph.nodes):
return cycle
return None
cycle = hamiltonian_cycle(G)
if cycle:
print("Hamiltonian Cycle:", cycle)
else:
print("No Hamiltonian Cycle found!")